The promise of
IGC-AD1
Findings from phase 1 study suggest that IGC-AD1 has the potential to safely reduce the debilitating symptoms affecting millions of Alzheimer’s patients.
IGC-AD1 Timeline
2017
IGC Pharma begins development of the IGC-AD1 oral formulation.
2019
IGC-AD1 is approved by the FDA as an investigational new drug.
2021
Phase 1 clinical trial testing safety and tolerability in humans with Alzheimer’s successfully completed.
IGC-AD1 is awarded patent protection in the U.S.

2022
Phase 2 clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of IGC-AD1 begins.
Additional patent awarded protecting IGC-AD1 formulation.

2023

2024

Why IGC-AD1 & Agitation in Alzheimer’s Dementia?
The APIs in IGC-AD1 have been associated with inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative stress markers associated with agitation in Alzheimer’s1.
The APIs in IGC-AD1 are proposed to reduce agitation by regulating impaired neurotransmission associated with agitation in AD pathology3,7.
The API have been shown to regulate cannabinoid CB1r imbalances in brain networks associated with aggressive behaviors in animal models4,6 and agitation in Alzheimer’s2.
IGC-AD1's Two APIs -
Multiple Modes of Action
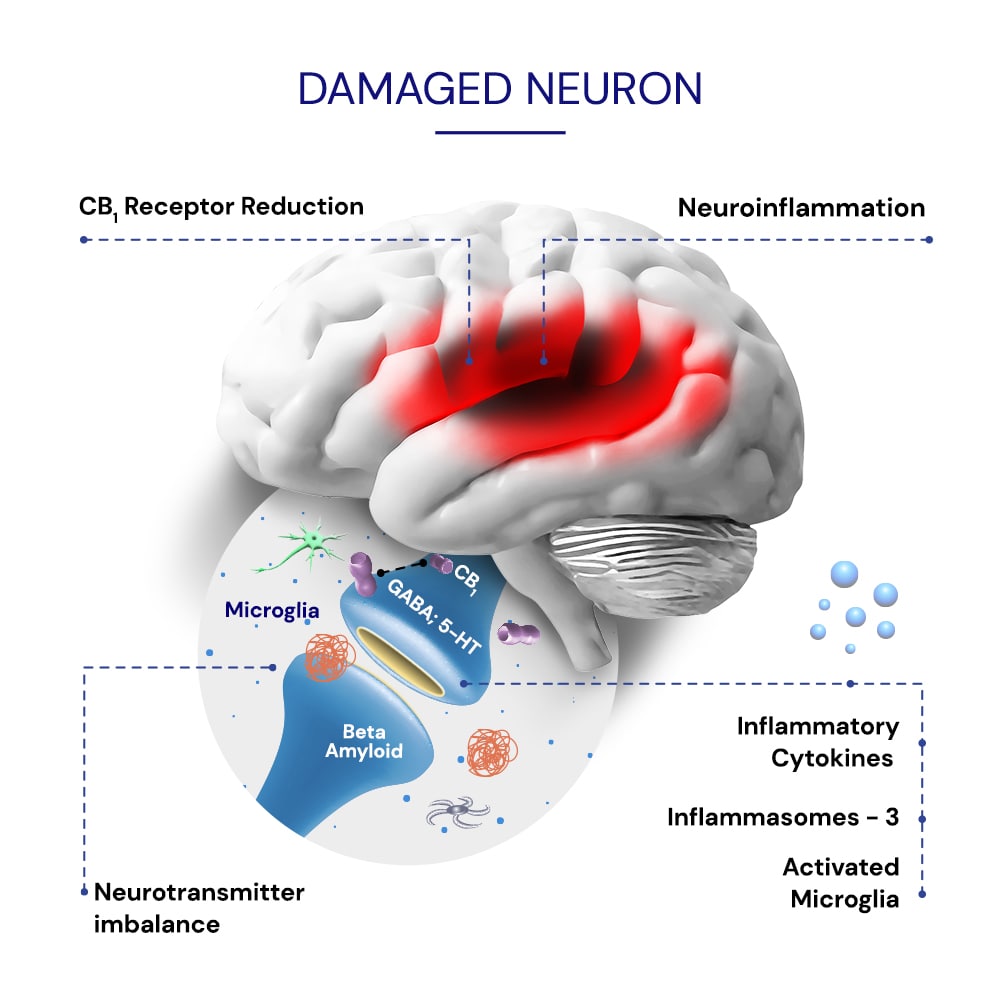
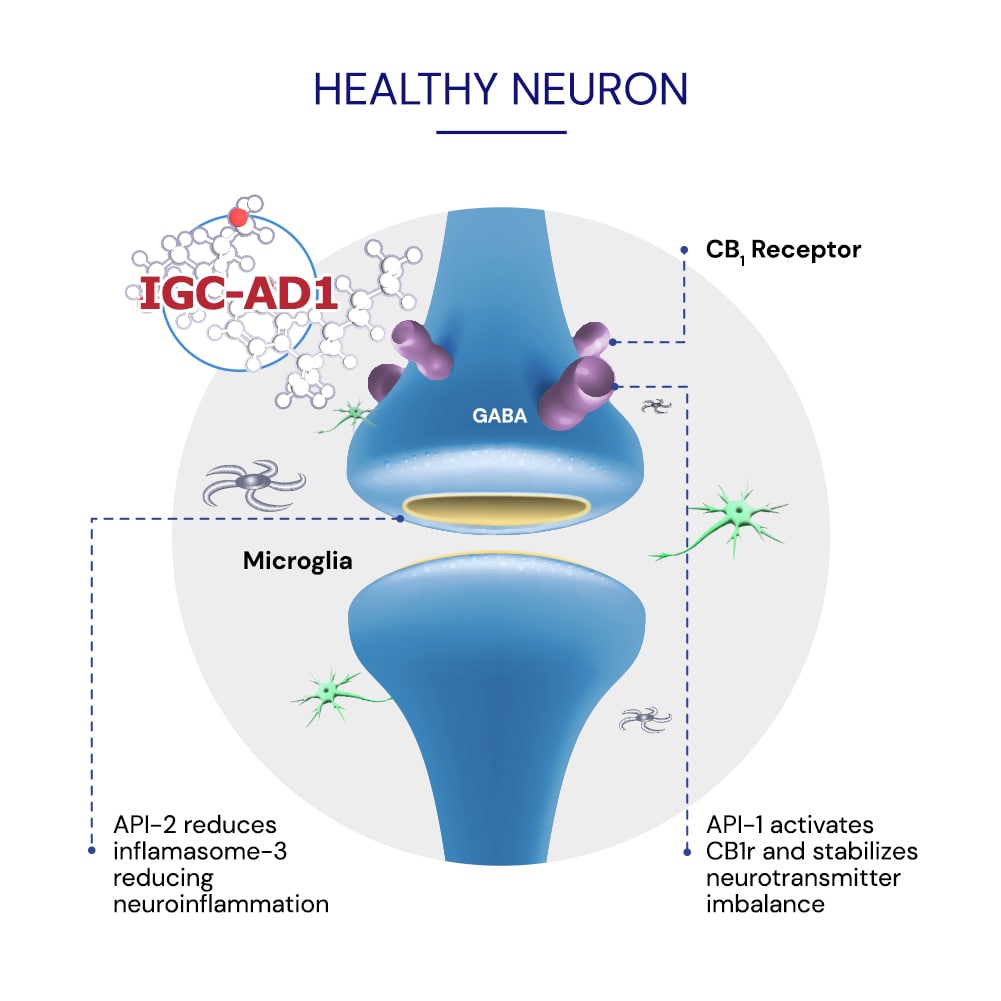
Pre-clinical
Phase I Clinical Trial
Study Design:
The study involved participants with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease to evaluate the safety and tolerability of IGC-AD1.
Results: IGC-AD1 was found to be safe and tolerable at three different dosage levels.
– Improvements were observed in Neuropsychiatric Symptoms (NPS) and Caregiver Distress.
Phase II Clinical Trial
brings hope
As millions of Alzheimer’s patients present agitation, our ongoing Phase 2 trial brings hope for a treatment.
Clinical trial includes up to 20 sites in the U.S. and Canada with a target of 146 participants.
As an oral liquid solution, IGC-AD1 could be an effective, simpler treatment option for patients
The API combination in the oral formulation is patent-protected
IGC-AD1 incorporates low concentration of a plant-derived API

- Yasuno F, Kimura Y, Ogata A, Ikenuma Abe J, Minami H, Nihashi T, Yokoi K, Hattori S, Shimoda N, Watanabe A, Kasuga K, Ikeuchi T, Takeda A, Sakurai T, Ito K, Kato T. Involvement of inflammation in the medial temporal region in the development of agitation in Alzheimer’s disease: an in vivo positron emission tomography study. Psychogeriatrics. 2023 Jan;23(1):126-135. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12915. Epub 2022 Nov 20. PMID: 36403981; PMCID: PMC10100091.
- Outen JD, Burhanullah MH, Vandrey R, Amjad H, Harper DG, Patrick RE, May RL, Agronin ME, Forester BP, Rosenberg PB. Cannabinoids for Agitation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2021 Dec;29(12):1253-1263. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2021.01.015. Epub 2021 Jan 27. PMID: 33573996; PMCID: PMC8313629.
- Lindenmayer JP. The pathophysiology of agitation. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000;61 Suppl 14:5-10. PMID: 11154018.
- Rosenberg PB, Nowrangi MA, Lyketsos CG. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: What might be associated brain circuits? Mol Aspects Med. 2015 Jun-Oct;43-44:25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 Jun 3. PMID: 26049034; PMCID: PMC4600424.
- Cao C, Li Y, Liu H, Bai G, Mayl J, Lin X, Sutherland K, Nabar N, Cai J. The potential therapeutic effects of THC on Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;42(3):973-84. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140093. PMID: 25024327.
- Rodriguez-Arias M, Navarrete F, Daza-Losada M, Navarro D, Aguilar MA, Berbel P, Miñarro J, Manzanares J. CB1 cannabinoid receptor-mediated aggressive behavior. Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:172-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Aug 2. PMID: 23916480.
- Roy J, Tsui KC, Ng J, Fung ML, Lim LW. Regulation of Melatonin and Neurotransmission in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6841. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136841. PMID: 34202125; PMCID: PMC8268832

