Preclinical:
The Research Powering IGC-AD1
IGC-AD1 springs from rigorous Preclinical testing and a people-first approach. In the lab, at low, non-toxic doses, its ingredient combination aimed to slow key Alzheimer’s Disease processes and showed encouraging signals.
Early Lab Discoveries
That Inspire Hope
Preclinical studies laid the groundwork for IGC-AD1 by testing its dual active ingredients in Alzheimer’s cell models and mouse models.
Preclinical Signals
in Mice
Mice treated with IGC-AD1 AP1 improved their spatial memory by about 50% and showed better mitochondrial function—crucial
Reduces Key
Alzheimer’s Features
The therapy decreased the buildup of amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques by 20% and maintained healthy APP levels in cell studies
Behavior-focused, with additional
Preclinical signals
In preclinical models, IGC-AD1’s ingredients showed better spatial memory performance and improved mitochondrial markers, alongside effects on Aβs.
The science behind IGC-AD1: early indicators
that matter for Alzheimer’s Disease research
-
Aβ Production
& Aggregation -
The API in IGC-AD1 reduces Aβ40 peptide production and Aβ42 aggregation in Alzheimer’s cell lines.
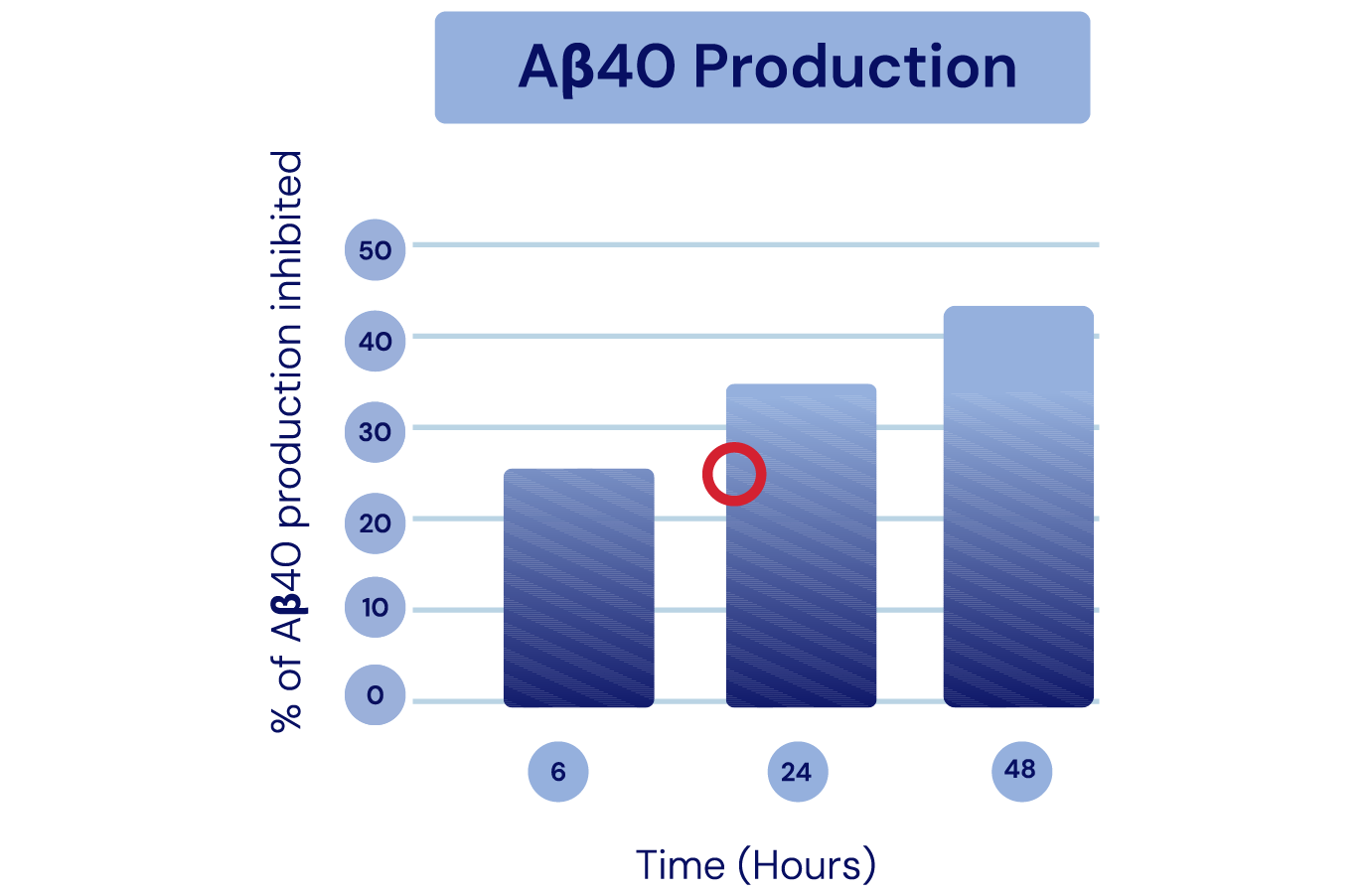 Representation of Cao et al., 2014
Representation of Cao et al., 2014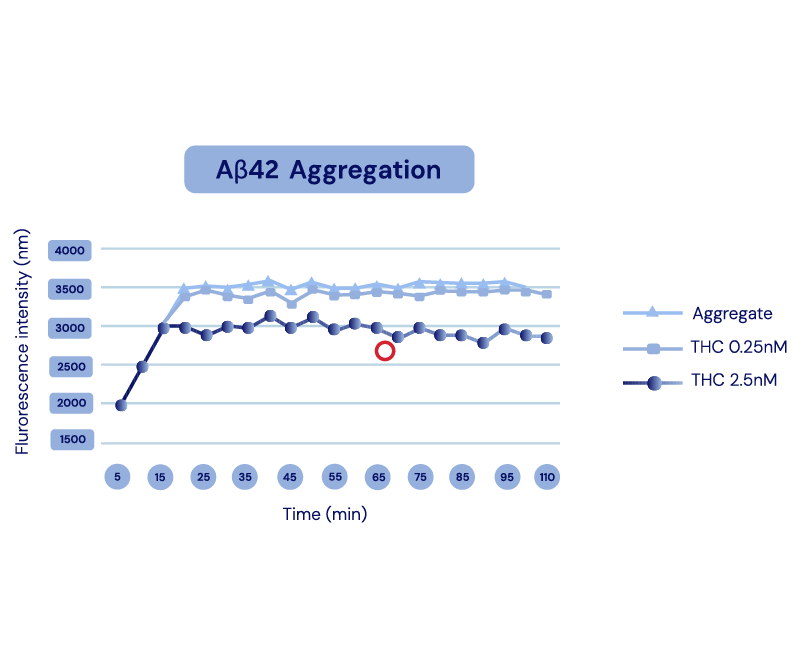
-
Aβ Monomers
-
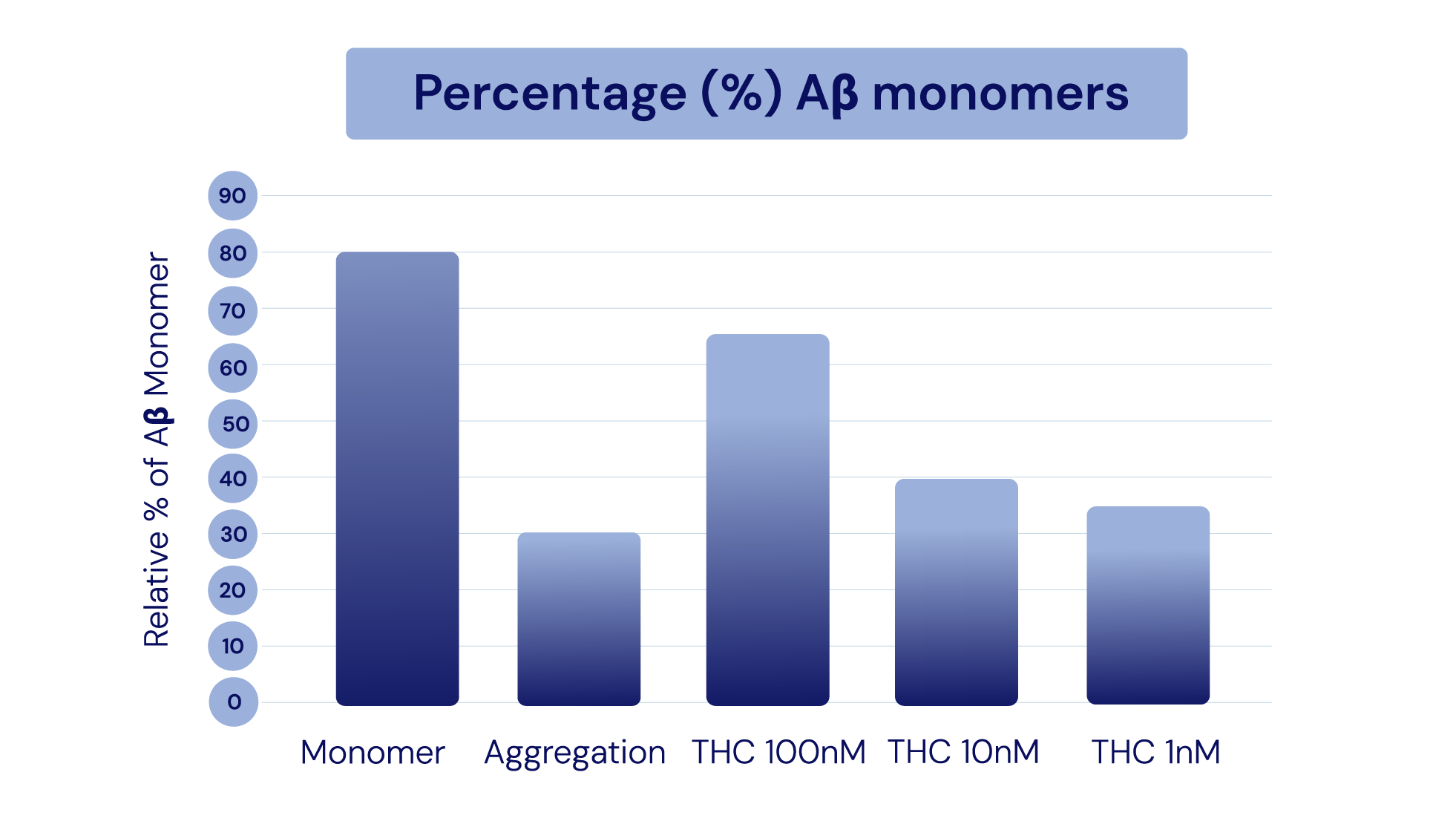 In Alzheimer’s cell lines, IGC-AD1 increased Aβ monomers and decreased Aβ aggregation in a dose-dependent manner.
In Alzheimer’s cell lines, IGC-AD1 increased Aβ monomers and decreased Aβ aggregation in a dose-dependent manner.Representation of Cao et al., 2014
-
APP Levels
-
The APIs in IGC-AD1 did not reduce Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) levels in Alzheimer’s cell lines. APP modulates cell growth, motility, and survival; it is cut to create small fragments such as the Aβ peptide that eventually deposit as plaque.
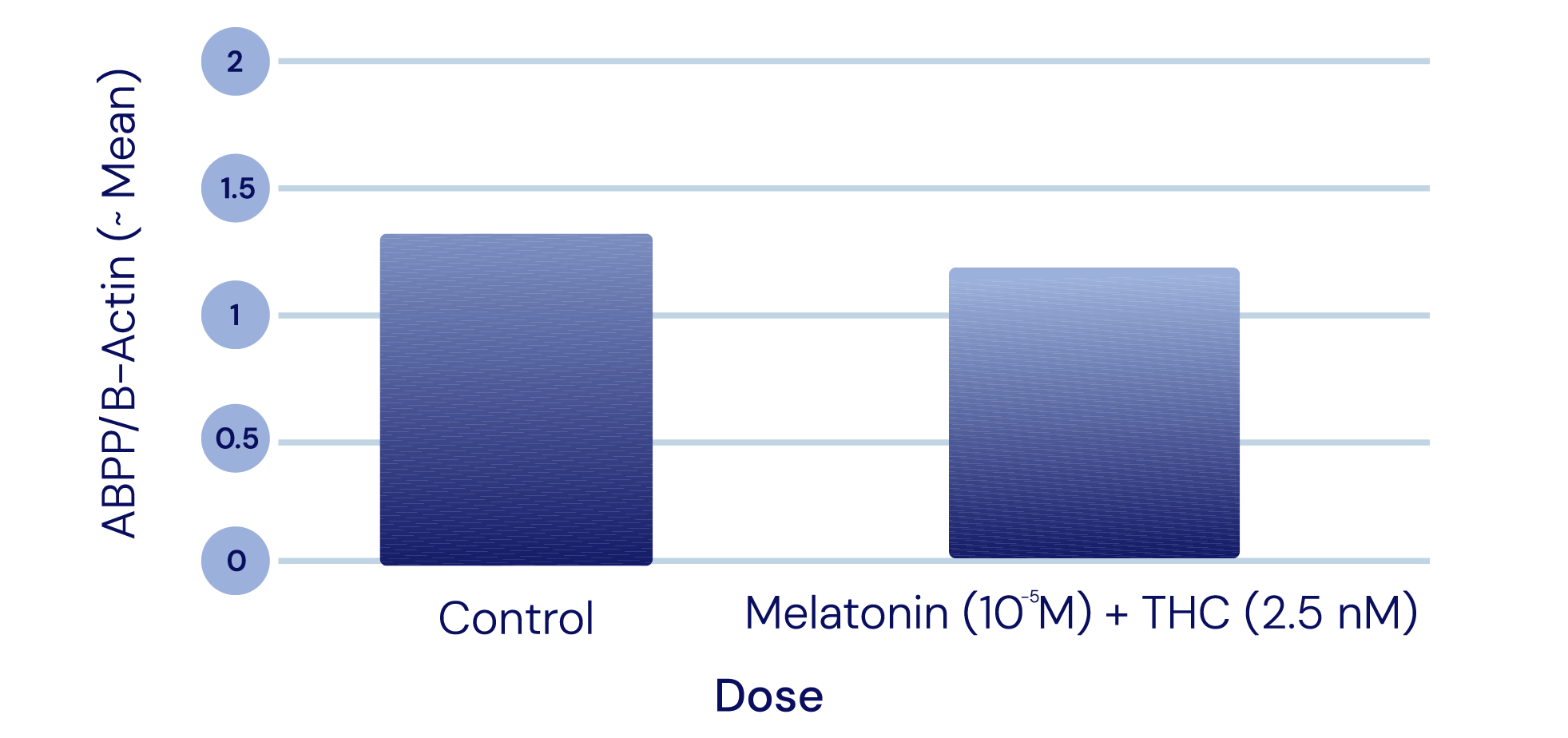 Representation of Cao et al., 2014
Representation of Cao et al., 2014 -
Spatial Memory
-
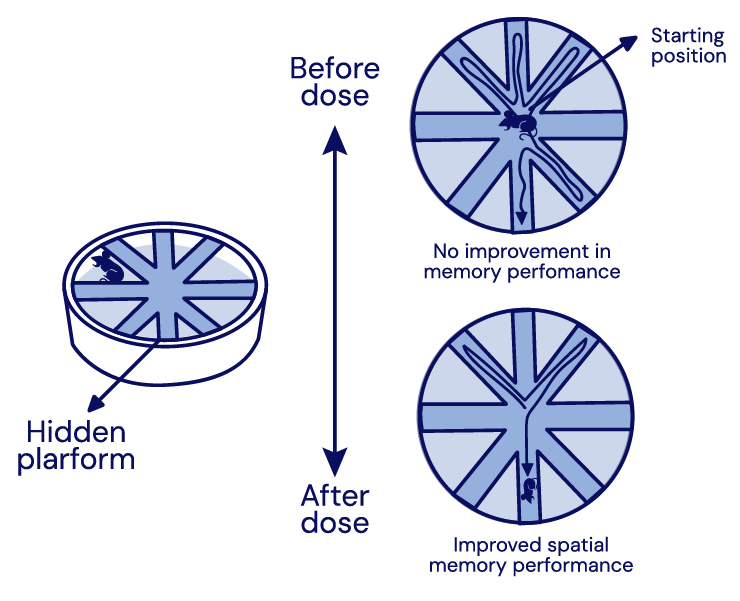
Memory Improved
in Alzheimer’s Mice ModelIn a Morris Water Maze test, mice dosed with the API in IGC-AD1 had significantly improved times and less errors than those in the control group demonstrating that memory improved in transgenic (APP/PS1) mice.
Nature Protocols. 2006; 1: 848-858; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2757 -
Neurotoxicity
-
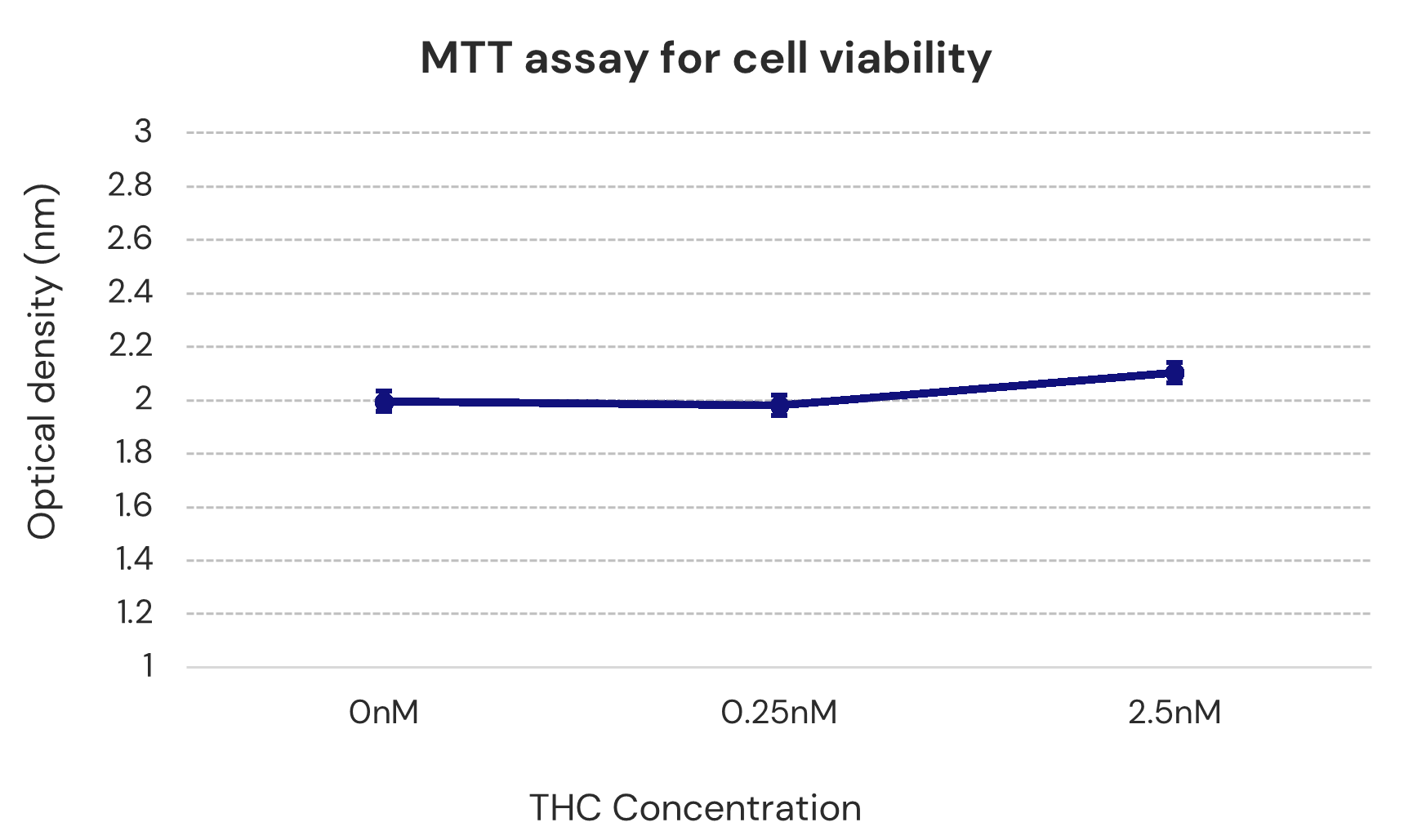 Over 48 hours, repeated low-dose exposure to the API in IGC-AD1 was not toxic to Alzheimer’s cells (N2a/AßPPsWe cells).Representation of Cao et al., 2014
Over 48 hours, repeated low-dose exposure to the API in IGC-AD1 was not toxic to Alzheimer’s cells (N2a/AßPPsWe cells).Representation of Cao et al., 2014



Representation of Cao et al., 2014


Memory Improved
in Alzheimer’s Mice Model
In a Morris Water Maze test, mice dosed with the API in IGC-AD1 had significantly improved times and less errors than those in the control group demonstrating that memory improved in transgenic (APP/PS1) mice.

